Invocations
An invocation is a request to execute a handler that is part of a Restate service.
There are three ways to invoke a handler:
HTTP requests
Send a request to the Restate Server (port 8080), with the handler name in the path, and the payload body.
Learn more
Programmatically
Use the SDK to send requests within Restate handlers. Or use generated HTTP clients anywhere else.
Learn more
Kafka events
Restate subscribes to a Kafka topic, and invokes a handler should for each message that arrives.
Learn more
All invocations are proxied through the Restate Server, which registers the request, routes the request to the correct handler, and drives the execution of the handler.
Invocations get a unique identifier. This identifier is used to track the progress of the invocation, and lets you correlate logs and metrics.
Invocation types
Request-response invocations allow you to call another handler and wait for the response.
Request-response invocations allow you to call another handler and wait for the response.
One-way invocations allow you to trigger an asynchronous action. This returns an invocation ID with which you can retrieve the result of the invocation later, if desired.
One-way invocations allow you to trigger an asynchronous action. This returns an invocation ID with which you can retrieve the result of the invocation later, if desired.
Delayed invocations allow you to schedule an invocation for a later point in time.
Delayed invocations allow you to schedule an invocation for a later point in time.
- TypeScript
- Java
- Go
- Python
- curl
async function myRestateHandler(ctx: restate.Context) {// From a Restate handlerconst greet = await ctx.serviceClient(greeter).greet({ greeting: "Hi" });}
const myFunction = async () => {// From any TypeScript/JavaScript functionconst restateClient = restate.connect({ url: "http://localhost:8080" });const greet = await restateClient.serviceClient(greeter).greet({ greeting: "Hi" });};
@Handlerpublic void myRestateHandler(Context ctx) {// From a Java Restate serviceString greet = GreeterServiceClient.fromContext(ctx).greet("Hi").await();}
public void myJavaHandler() {// Or from any other Java programClient restateClient = Client.connect("http://localhost:8080");String greet = GreeterServiceClient.fromClient(restateClient).greet("Hi");}
func (MyService) MyRestateHandler(ctx restate.Context) (string, error) {greet, err := restate.Service[string](ctx, "Greeter", "Greet").Request("Hi")return greet, err}
@my_service.handler()async def my_handler(ctx: Context, arg):greeting = await ctx.service_call(greet, arg="Hi")
curl localhost:8080/GreeterService/greet --json '"Hi"'
Learn more about HTTP invocations, SDK clients, Kafka events.
Idempotent invocations
You can add an idempotency key to your request header to make the invocation idempotent. Restate will then deduplicate requests with the same idempotency key, and will only execute the handler once. Duplicate requests will get the same response as the first request, or will latch on to the first invocation if it's still running.
curl localhost:8080/GreeterService/greet \-H 'idempotency-key: ad5472esg4dsg525dssdfa5loi' \--json '"Hi"'
Inspecting invocations
Restate proxies and manages inbound as well as service-to-service invocations. This makes it a great source of observability data for your application. You can inspect invocations via the UI:
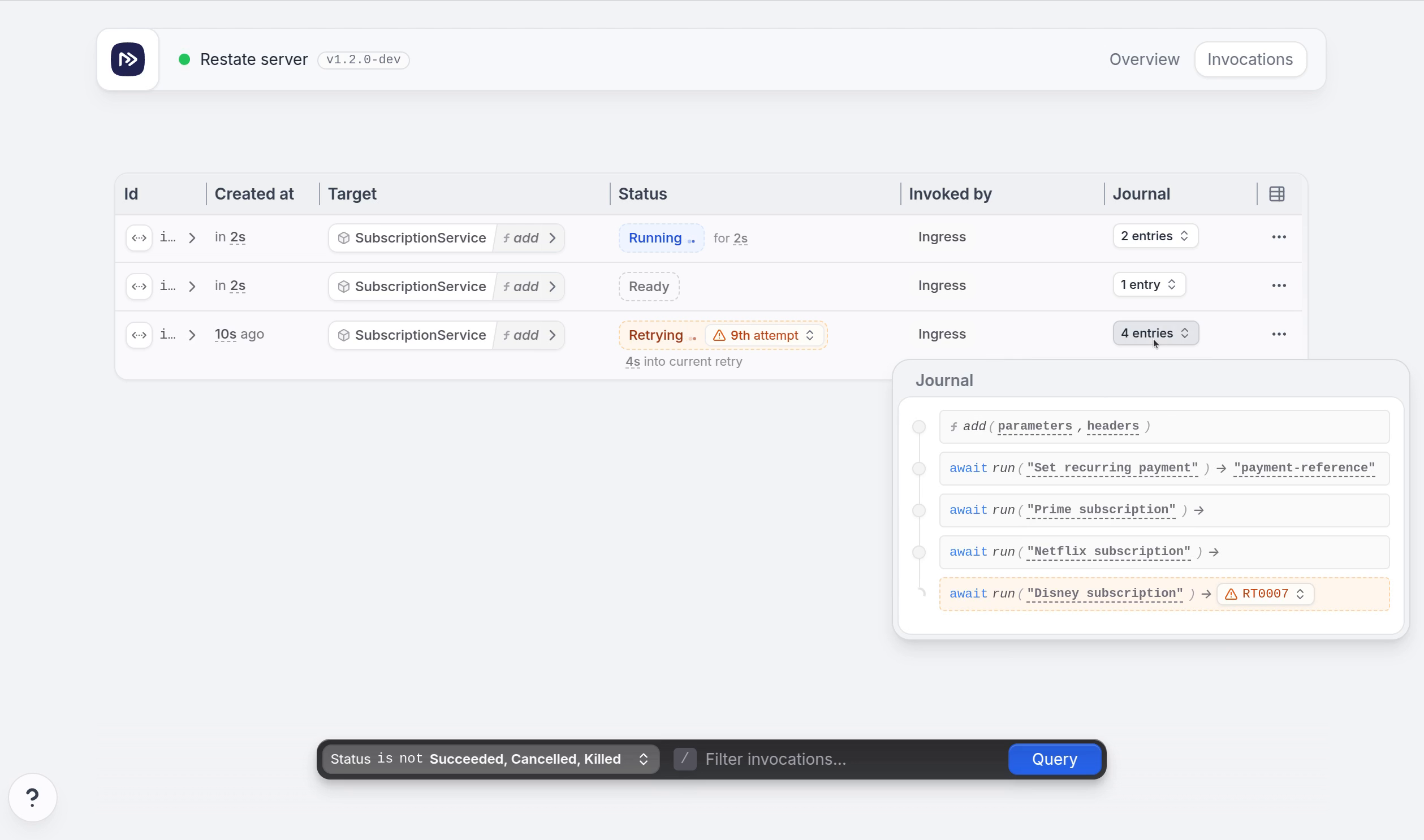
Or via the CLI:
restate services list
restate services describe CartObject
restate invocations list
restate invocations describe inv_1fmRNvSNVxNp5PTqHI4HLJ17HpxzhB3MEV
Restate also exposes traces via OpenTelemetry, which can be sent to your observability platform of choice (e.g. Jaeger).


Cancelling and killing invocations
You can cancel and kill invocations via the Restate UI, the CLI, or with the SDK clients.
- For cancellations, Restate will gracefully stop the handler by executing all compensation actions.
- For kills, Restate will immediately stop the handler without executing any compensation actions.
If necessary, you can register compensating actions in your handlers to ensure that the system remains consistent amid cancellations (sagas guide).
restate invocations cancel --kill inv_1fmRNvSNVxNp5PTqHI4HLJ17HpxzhB3MEV